Understanding Fidelity Bond Insurance: Banks Against Internal Risks Leave a comment
Introduction In the complex ecosystem of banking, trust is paramount. Customers trust banks with their hard-earned money, and shareholders trust banks to protect and grow their investments. However, within the confines of any institution, there exists the potential for internal risks – be it fraud, embezzlement, or dishonesty.
Fidelity bond insurance emerges as a critical tool in mitigating these risks, providing financial protection against losses arising from acts of dishonesty by employees. This article aims to delve into the depths of fidelity bond insurance for banks, exploring its intricacies, significance, and relevance in the contemporary financial landscape.
Understanding Fidelity Bond Insurance Fidelity bond insurance, often referred to as fidelity insurance or simply fidelity bonds, is a specialized form of insurance designed to protect an organization from losses incurred due to fraudulent or dishonest acts committed by its employees. In the context of banking, fidelity bond insurance serves as a safeguard against internal risks that could potentially threaten the financial stability and reputation of the institution.
Key Features of Fidelity Bond Insurance for Banks
Coverage: Fidelity bond insurance typically covers various forms of employee dishonesty, including theft, forgery, fraud, and embezzlement. The coverage extends to both tangible assets, such as cash and securities, and intangible assets, such as confidential information and intellectual property.
Insured Parties: Banks, as the insured entities, purchase fidelity bond insurance to protect themselves against losses resulting from the dishonest actions of their employees. The coverage may also extend to third parties, such as customers or clients, who suffer financial harm due to employee misconduct.
Limits and Deductibles: Fidelity bond insurance policies specify coverage limits, which represent the maximum amount the insurer will pay in the event of a covered loss. Additionally, policies may include deductibles, requiring the insured bank to bear a portion of the losses before the insurance coverage takes effect.
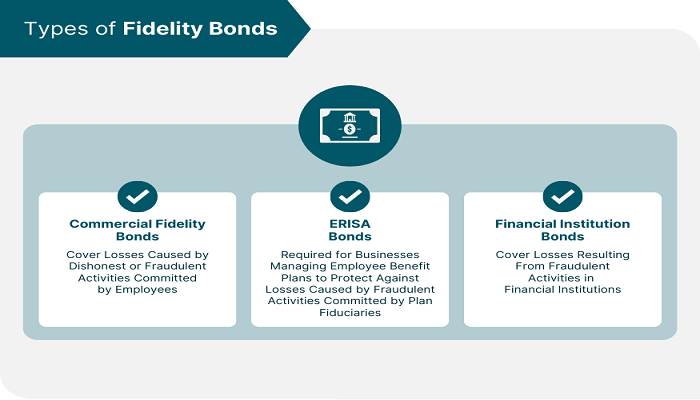
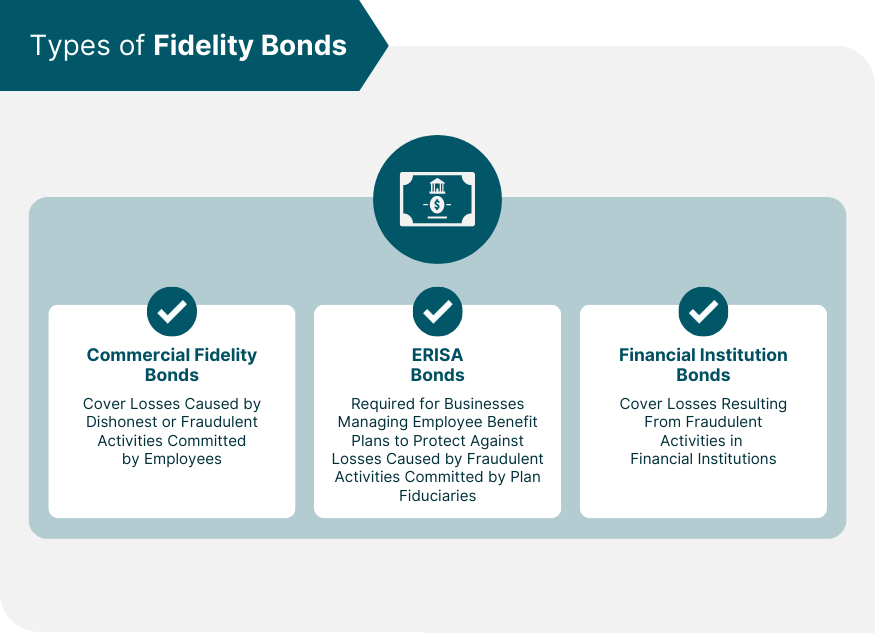
Types of Bonds: Fidelity bonds come in various forms, tailored to the specific needs and risk profiles of banks. Common types include first-party bonds (protecting the insured bank itself), third-party bonds (protecting customers or clients), and blanket bonds (providing broad coverage across multiple employees and positions).
Importance of Fidelity Bond Insurance for Banks
Risk Mitigation: Banks face inherent risks associated with the handling of large sums of money and sensitive financial information. Fidelity bond insurance serves as a critical risk management tool, providing financial protection against the potential fallout from internal fraud or dishonesty.
Regulatory Compliance:
Regulatory authorities often mandate banks to maintain fidelity bond insurance as part of their risk management and compliance frameworks. Compliance with these requirements demonstrates the bank’s commitment to safeguarding the interests of its stakeholders and maintaining the integrity of the financial system.
Protecting Reputation:
Any instance of internal fraud or misconduct can severely damage a bank’s reputation and erode the trust of its customers, shareholders, and the public at large. Fidelity bond insurance helps mitigate the financial repercussions of such incidents, enabling banks to uphold their reputation as trustworthy financial institutions.
Enhancing Stakeholder Confidence:
By securing fidelity bond insurance, banks reassure their stakeholders – including depositors, investors, and regulatory authorities – that they are proactively addressing the risks associated with employee dishonesty. This, in turn, fosters confidence in the bank’s operations and governance practices.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples To illustrate the significance of fidelity bond insurance in the banking sector, let us consider a few real-world examples:
XYZ Bank: In 20XX, XYZ Bank discovered that one of its employees had been siphoning funds from customer accounts for personal gain. Thanks to its fidelity bond insurance coverage, the bank was able to recoup a significant portion of the losses and restore customer trust through transparent communication and restitution efforts.
ABC Credit Union: Following an internal audit, ABC Credit Union uncovered instances of check fraud perpetrated by a group of employees. Despite the substantial financial losses incurred, the credit union’s fidelity bond insurance policy provided the necessary coverage to mitigate the impact on its operations and member accounts.
DEF Investment Firm: DEF Investment Firm fell victim to a sophisticated phishing scheme orchestrated by a rogue employee, resulting in unauthorized wire transfers and securities transactions. Fortunately, the firm’s fidelity bond insurance policy included coverage for cyber-related fraud, enabling swift recovery and reinforcing its cybersecurity protocols.
Conclusion:
Fidelity bond insurance stands as a cornerstone of risk management within the banking industry, offering essential protection against the threats of internal fraud, embezzlement, and dishonesty. By investing in comprehensive fidelity bond coverage, banks can fortify their defences, preserve their financial stability, and uphold the trust and confidence of their stakeholders.
In an era marked by evolving regulatory landscapes and emerging cyber threats, fidelity bond insurance remains an indispensable tool for safeguarding the integrity and resilience of the global banking system.
